Lecture #01: Course Introduction and the Relational Model
Relational Model
The relational model defines a database abstraction based on relations to avoid maintenance overhead.
Key tenets:
- Store database in simple data structures(relations).
- Physical storage left up to the DBMS implementation.
- Access data through high-level language, DBMS figures out best execution strategy.
n-ary Relation = Table with n columns
Relational Algebra: JOIN

Databases are ubiquitous.
Lecture #02: Advanced SQL
SQL is based on bags(duplicates) not sets(no duplicates).
Group By
Non-aggregated values in SELECT output clause must appear in GROUP BY clause.

为了快速学完直接看slides的,发现SQL部分还是有不懂的地方,居然想着得过且过😳,不会就跳过吧。幸好看了video,Easy has a cost. 不要偷懒,多重复几次总会搞懂的。
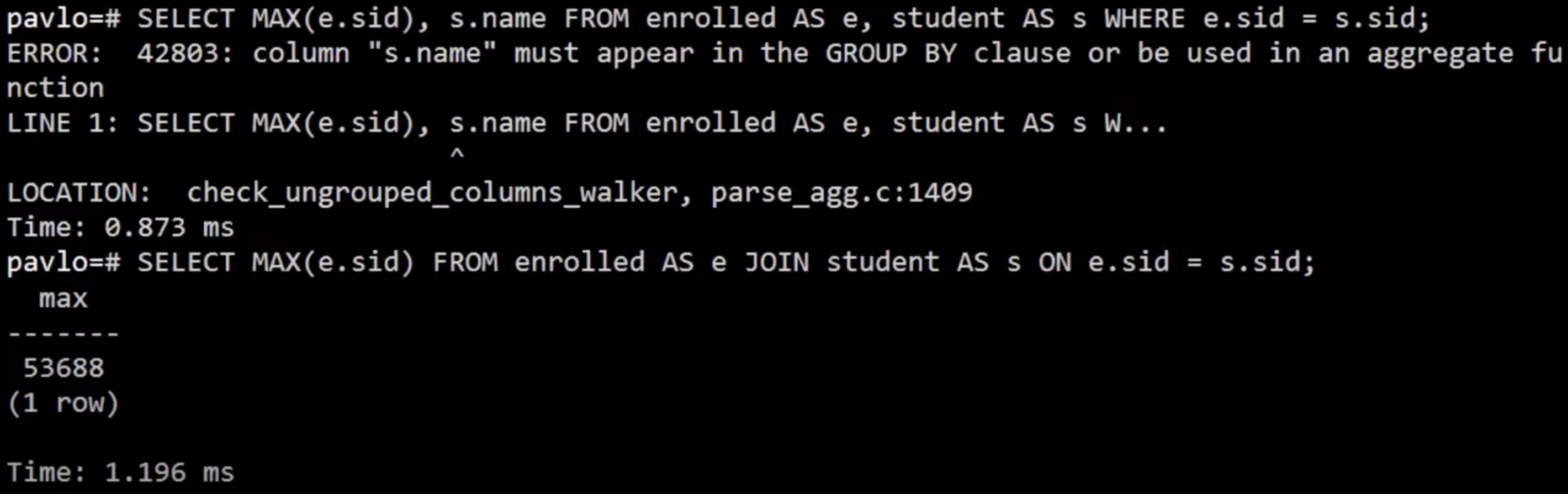
MySQL:
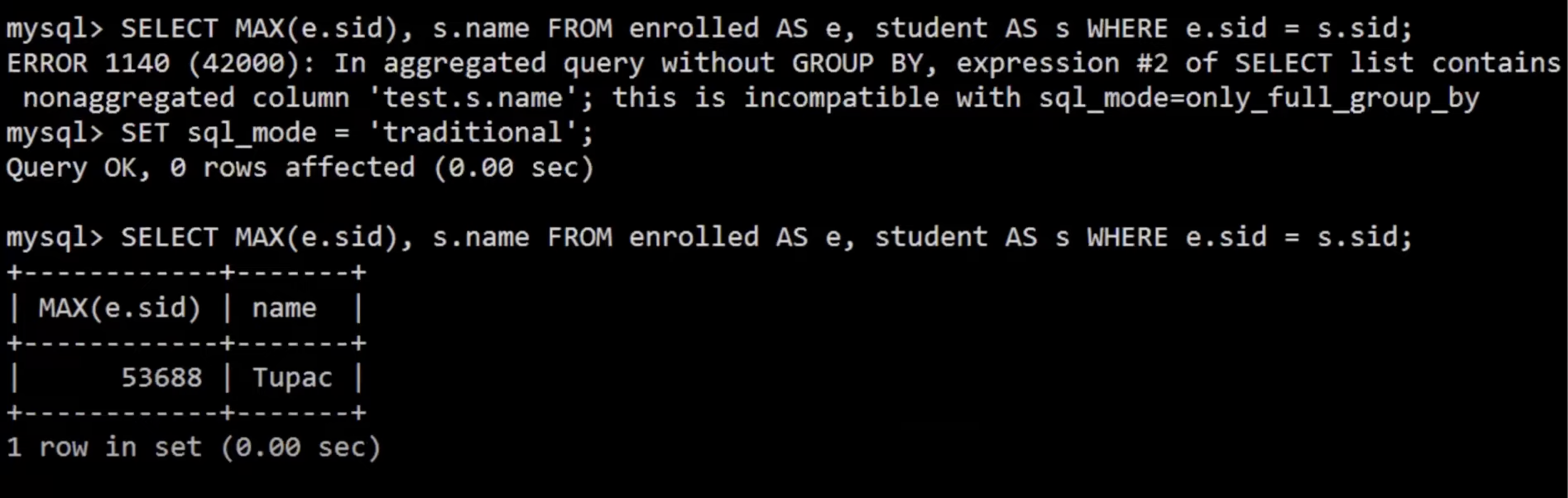
切换到MySQL之前的版本可以用该语句查询,但其实结果不正确。
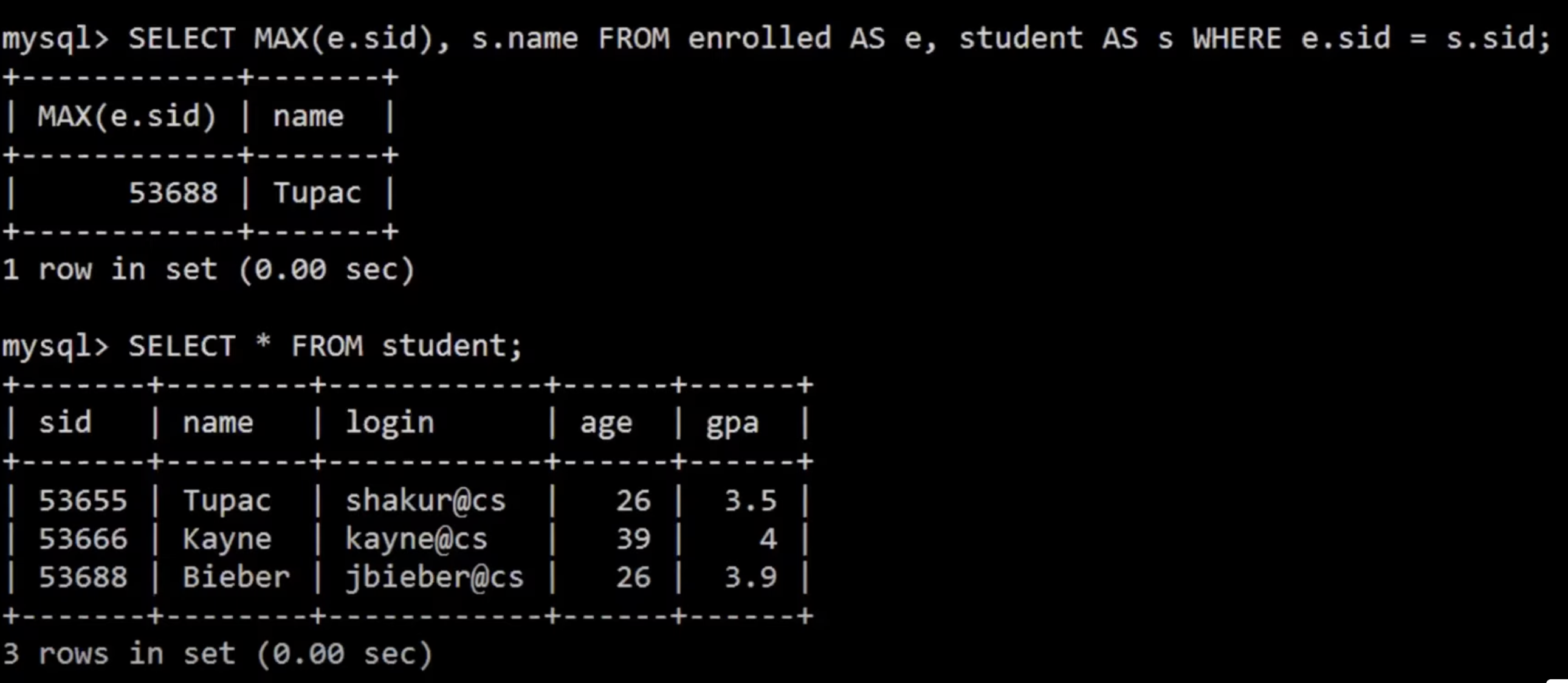
查询student表,发现结果是错误的。
看了video知道哪里错了,还是要多实践。Andy会在课堂演示,想起了本科一位年轻教师(为数不多会在课堂拿自己笔记本电脑写代码投屏给我们看的),也是位好老师。
Homework 1: SQL
Q10没搞懂意思,所以只有85/100。
Lecture #03: Database Storage I
Sequential VS. Random Access
DBMS will want to maximize sequential access.
Allocating multiple pages at the same time is called an extent.
memory mapping(mmap)❌
The DBMS can use memory mapping(mmap) to store the contents of a file into the address space of a program.
Unfortunately, this means that if mmap hits a page fault, the process will be blocked.
What if we allow multiple threads to access the mmap files to hide page fault stalls?
This works good enough for read-only access. It is complicated when there are multiple writers…
solutions:
- madvise: Tell the OS how you expect to read centrain pages.
- mlock: Tell the OS that memory ranges cannot be paged out.
- msync: Tell the OS to flush memory ranges out to disk.
哈哈哈,slides中有“The OS is not your friend.”,这是DB调侃OS嘛😂。
File Storage
Three different notions of “pages” in a DBMS:
- Hardware Page(usually 4kB)
- OS Page(usually 4KB)
- Database Page(512B-16KB) 发现Database Pages的大小差异好大。
Page Layout
1. Slotted-pages
- Page maps slots to offsets.
- Header keeps track of
- the number of used slots
- the offset of the
starting locationof thelast used slot - a slot array: the location of the
startof each tuple
- To add a tuple
- the slot array will grow from the beginning to the end
- the data of the tuples will grow from end to the beginning
2. Log-structured
- Only store log records
- Fast writes, potentially slow reads(DBMS can have indexes to avoid long reads)
- periodically compact the log——> the DBMS ends up with write amplification
Tuple Layout
Tuple Header: Contains meta-data about the tuple
Tuple Data: Actual data for attributes
Unique Identifier
Record IDS
Each tuple is assigned a unique record identifier.
- most common: page_id+offset/slot
- Can also contain file location info
An application cannot rely on these IDs to mean anything. 不太懂什么意思?
Lecture #04: Database Storage II
Data Representation
Lager vaues
DBMS uses separate overflow storage pages.
External vaule storage
external file treated as a BLOB type.
The DBMS cannot manipulate the contents of an external file.
- No durability protections
- No transaction protections
System catalogs
A DBMS stores meta-data about databases in its internal catalogs.
- Tables, columns, indexes, views
- Users, permissions
- Internal statistics
Lecture #05: Storage Models & Compression
N-ary storage model
cons:
- Fast inserts, updates, and deletes
- Good for quries that need the entire tuple
pros:
- Not good for scanning large portions of the table and/or a subset of the attributes
Decomposition storage model(DSM)
“column store”: stores the values of a single attribute for all tuples contiguously in a page.
cons:
- Reduce the amount wasted I/O
- Better query processing and data compression
pros:
- Slow for point queries, inserts, updates, and deletes because of tuple splitting/stitching
Compression Granularity
Block-Level
Tuple-Level
Attribute-Level
Column-Level
Columnar Compression
Run-Length Encoding
- RLE Triplet: (Value, Offset, Length)
Bit-Packing Encoding
- look-up table
Bitmap Encoding
- The
ith position in the Bitmap <——>ith tuple in the table - Only practical if the value cardinality is low.
Delta Encoding
- Recording the difference values that follow each other in the same column
Incremental Encoding
- avoids duplicating common prefixes/suffixes between consecutive tuples
- works best with
sorted data
Dictionary Encoding
- Build a data structure
- maps
variable-lengthvalues ——> asmaller integer identifier - Most widely used compression schema in DBMSs
Conclusion
OLTP=Row Store
Fastoperations that onlyread/updateasmallamount of data each time
OLAP=Column Store
- Complex queries that read
a lot of datato compute aggregates
Project 0: C++ Primer
Project 1: Buffer Pool Manager
Homework 2: Storage & Indexes
Storage Models
Cuckoo Hashing
Extendible Hashing
B+Tree
有在iPad上手写认真做。